- Home
- All Posts
- Flow Battery
- Zinc-air Flow Battery
- Overview of Zinc-air Flow Batteries(ZAFBs)
Blog

Overview of Zinc-air Flow Batteries(ZAFBs)
Principle of zinc-air flow batteries
There are two electrodes in zinc-air battery, which are Zn(-) and 02(+), cathode and anode are separated and ions can transfer in the battery. Potassium hydroxide (KOH) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) are commonly used electrolytes, however KOH is popular because it offers ideal ionic conductivity for battery. At the anode (- electrode), generally Consist of zinc powder, zinc plate, zinc foil, etc, Zinc reacts with hydroxide ions(OH-) to form zincate ions, and then zinc oxide (ZnO) precipitation reaction occurs when concentration of zincate ion increases to the limit of its solubility. Hydrogen evolution reaction(HER) proceeds on Zn electrode, water electrolysis convert H2O into hydrogen (H2) and hydroxide ions, and HER dissolution reaction will lead to corrosion on Zn. The relationship shown in equation as follow:
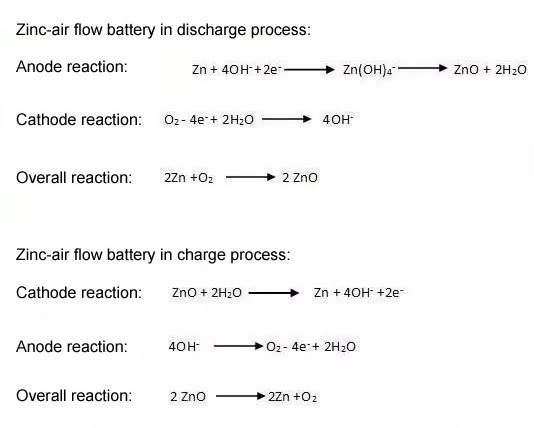
At the cathode (+ electrode),Generally consists of diffusion layer, current collector and catalytic layer, oxygen rective reaction(ORR) and oxygen evolution reaction(OER) occurs during process of charging and discharging. Because zinc-air battery uses inexhaustible oxygen as active material for positive electrode, the energy level of cell mainly depends on anode metal zinc plate.
Advantages of ZAFBs
1) Cheap raw material and simple manufacturing process. Currently, the proven zinc mines in China reserves ranks the first in the world. Even in the world, the mining and production costs of zinc are cheaper than other metals, compares to lithium carbonate or lithium hydroxide materials in lithium batteries, the cost is only one tenth. The active material oxygen on the positive electrode can be obtained directly from the air without any cost. As a mature technology, The production process of ZAFBs generally uses semi-mechanized method, and the manufacturing process is relatively easy.
2) High energy density and large cell capacity. We know that the active material on + electrode of zinc batteries is oxygen which can be obtained from air, so most of the space inside battery can be used to fill more negative electrode zinc materials. Therefore, under the same weight, the capacity of zinc air flow battery is larger than that of other types of batteries. The theoretical energy density of ZAFBs can reach 1350WH/KG, and in practical applications, it has also reached 200 to 300WH/KG, which is almost the theoretical limit of ternary lithium batteries.
3) Stable performance and reliable. The air electrode on positive electrode won’t change during discharge, and zinc on negative electrode is gradually consumed during the oxidation process. The overall redox reaction is slow and the voltage changes smoothly. When the cell is not in use, the air inlet can be closed to isolate air electrode. As long as air is not able to enter into zinc air flow battery, there will be no electrochemical reaction and little capacity loss.
4) Environmentally friendly and safe. Zinc-air flow batteries have abandoned traditional toxic substances such as lead, mercury and cadmium. The positive electrode generally uses activated carbon and copper mesh, and the negative electrode uses metallic zinc, which is a non-toxic and pollution-free raw material. The reactant is zinc oxide during use, which can be easily recycled. In addition, the internal components are not flammable, even for short circuit or puncture accident, the leaked electrolyte will not burn or explode.
Disadvantages of ZAFBs
1) Charging and discharging problems. Due to the constant consumption of Zn, the replacement of zinc and electrolyte is necessary for continuous use, which is difficult in maintenance and can’t cycle charge like lithium batteries. Besides, zinc dendrites is formed during long-term charging and discharging process, and they will grow continuously, and then penetrate the membrane, cause short circuit issues. The heat generated during high current discharge can also affect the performance of battery.
2) Cell sealing issues. If the quality of the waterproof membrane is poor, there are many risks caused by the pores on cell shell, such as electrolyte leakage, moisture evaporation and absorption, which can affect the concentration of electrolyte. The semi-open structure also allows external CO2 to enter into the cells, result in carbonatization in electrolyte, greatly increase internal resistance of cell and reduce battery quality.
3) High self-discharge rate. The zinc electrode will dissolve and self-discharge in an alkaline solution with release of H2, resulting in loss of electricity. The uneven surface of zinc electrodes can also lead to differences on electrochemical activity in different areas. The difference in potential is equivalent to produce many micro cells inside, and accelerate the corrosion of zinc in the battery.
4) The redox ability of catalyst. The catalysts in air electrode are still the shortcoming of zn batteries. Voltage, efficiency and service life are limited by the redox capabilities of different catalysts. In some anoxic plateau zones and unventilated areas, it’s hard to obtain sufficient oxygen to generate enough electricity.
Prospect of zn-air flow battery
At present, industrialized zn air battery applications are mainly is mainly focused on the market for disposable batteries such as square or button batteries, but there is no breakthrough in cylindrical batteries with strong demand. United States and Canada started study of ZAFB earlier and have more advanced research results, and claimed that the cycle life can reach more than 5000 and the energy efficiency can reach 75%. Many domestic companies and research organizations have also begun to work on development of ZAFB, however there is still a long way to achieve commercialization. Taking the automotive market as an example, Wuhan launched a new energy vehicle equipped with zinc air flow batteries in 2012. Although the price is only one-third of that of lithium battery buses, the endurance is also higher. Up to now, it’s impossible to change the technical route of li battery power, and basically no possibility of batch assembly. The ultimate reason is that there is no breakthrough in technical bottleneck. For example, replacing zinc cell or electrolyte requires professional personnel and specialized equipment, that means huge investment is needed in earlier stage. Car manufacturers dare not blindly bet until public supporting industries are well developed. On the other hand, the investment layout related to lithium batteries has been fully launched, and occupies most share of market. Therefore, the future development direction of zinc air flow battery should be to break through the technical difficulties and strive to have a place in large-scale energy storage or emerging fields.
About Mr. Zhou
Search
Recent Posts
-
Manufacturing Process of Ca... 11/28/2024
-
Application of Flexible Gra... 05/14/2024
-
PEM Water Electrolysis for ... 04/12/2024
-
Application of Bipolar Memb... 01/09/2024
-
Membrane Electrode Assembly... 11/27/2023
Categories
- All Posts (24)
- Flow Battery (11)
- Battery Material (20)
- Bipolar Plate (13)
- Membrane (3)
- Felt Electrode (1)
- MEA (3)
- Fuel Cell (5)
Contact Info.
Recent Post
-
Manufacturing Process of Ca... 11/28/2024
-
Application of Flexible Gra... 05/14/2024
-
PEM Water Electrolysis for ... 04/12/2024
-
Application of Bipolar Memb... 01/09/2024
-
Membrane Electrode Assembly... 11/27/2023